

|
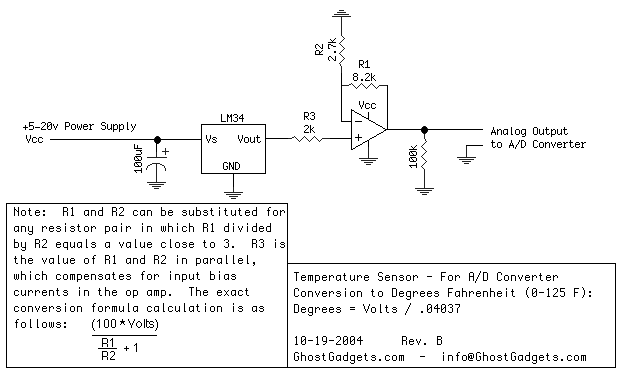
This is a simple, yet effective temperature meter, designed to give an analog DC output of 0-5 volts, proportionate to the surface temperature of the LM34. This is the same circuit design I use for Arcadia's surface temperature meter, and for the cost of construction (just a few dollars from DigiKey), it is a great meter. The circuit design is simple - the LM34 puts out 10mv per degree F, which then goes through a non-inverting amplifier. The signal is amplified 4 times, to give an output of 0 to 5 volts, from temperatures ranging from 0 to 125 degrees fahrenheit. Any discrete op amp will do - I have found LM358's to be very reliable and accurate for these type of meters, and can read almost to ground from a single power supply. The power supply can be from a power transformer, 9 volt battery, or any other 5-20 volt source. Also, as noted on the schematic, R1 and R2 can be interchanged for any resistor values that have a ratio close to 3. R3 is the value of R1 and R2 in parallel, (R1*R2) / (R1 + R2), which compensates for non-ideal input bias currents in the op amp. I have provided the basic conversion equation (assuming ideal resistor values) on the right of the schematic, but to obtain the most accurate conversion, use a Digital Multimeter to measure the values of R1 and R2 directly, and plug them into the formula given on the left of the schematic. Mounting the LM34 is described below, in an excerpt from the LM34's datasheet. |